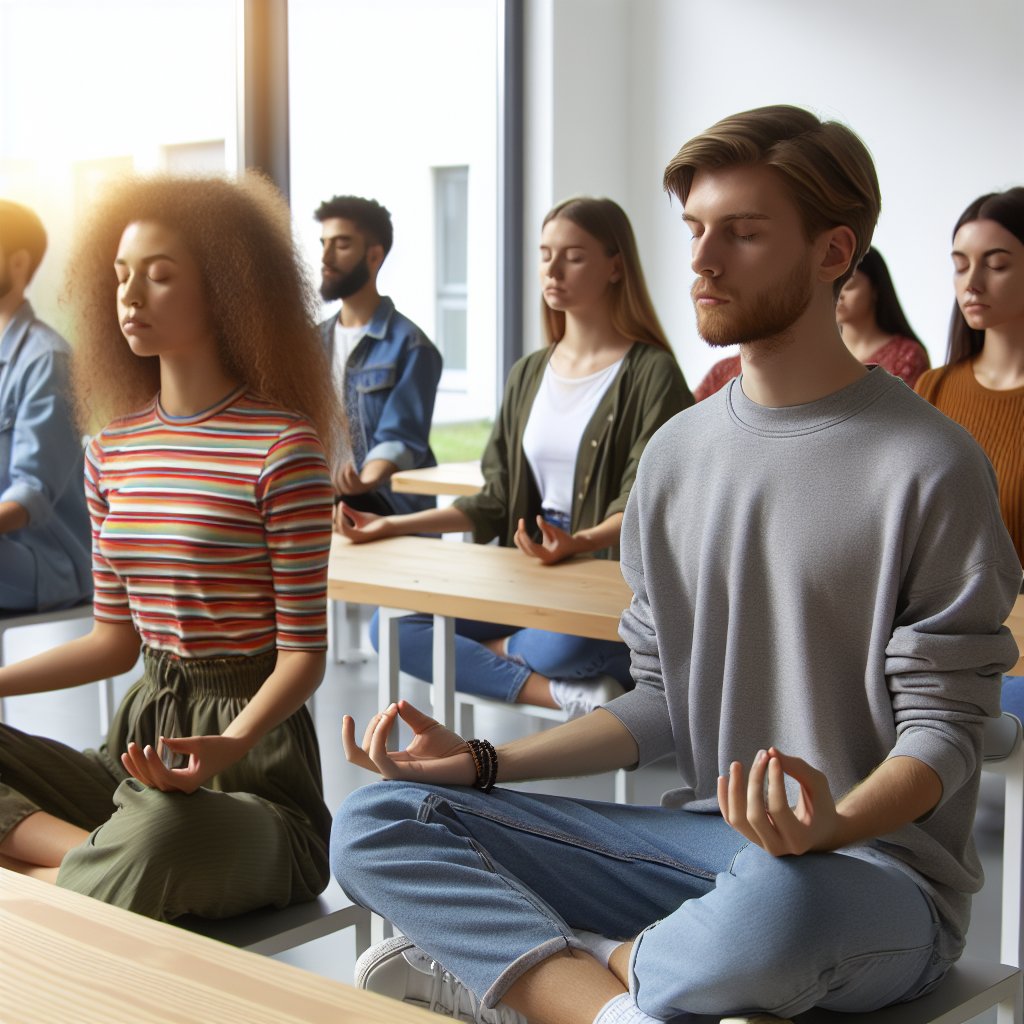
Classroom Mindfulness Techniques for Improved Cognitive Focus are becoming an important part of modern education strategies. As distractions grow and student attention spans shrink, teachers are increasingly turning to mindfulness to help learners stay present, reduce stress, and improve learning outcomes.
Why Classroom Mindfulness Techniques for Improved Cognitive Focus Matter
Many teachers notice that students struggle with focus, especially with the growing influence of smartphones and digital overload. When students can’t concentrate during lessons, their ability to retain knowledge drops significantly. That’s where mindfulness comes in. Implementing simple mindfulness techniques in a classroom setting can enhance attention, emotional regulation, and even classroom behavior.
Mindfulness, at its core, means intentionally paying attention to the present moment without judgment. This mental shift supports greater awareness and less reactivity, which can benefit both academic performance and emotional well-being.
How Classroom Mindfulness Techniques for Improved Cognitive Focus Work
These techniques aren’t about forcing students into long sessions of quiet meditation. Instead, they involve quick, guided practices that help students center their minds before or during classroom activities. Over time, these brief moments of mindfulness can create lasting changes in how students approach learning and stress.
Research suggests that when students practice mindfulness regularly, their prefrontal cortex — the brain region responsible for decision-making and attention — becomes more active and resilient. This not only helps in the classroom but can improve life outside of school as well.
Practical Mindfulness Tools for the Classroom
Mindfulness strategies can be tailored to different grade levels and student needs. Here are some effective tools teachers can integrate without disrupting their teaching schedule.
- Mindful Breathing: Guide students through a 1 to 2-minute breathing exercise where they focus on inhaling and exhaling slowly. This is especially useful before tests or after recess.
- Body Scans: Lead students in noticing physical sensations from head to toe. This helps ground them in the present and can calm pre-lesson jitters.
- Mindful Listening: Play a sound, like a bell or a simple nature clip, and have students listen until the sound fades away. Then ask them to describe what they heard.
- Gratitude Moments: Encourage students to reflect on one thing they’re thankful for at the start of the day. It promotes a positive mindset and builds emotional intelligence.
- Silent Reflection Time: Offer a minute or two after a lesson for students to process and reflect silently. This enhances memory retention and respect for personal space.
Health Connections in Student Mindfulness Practice
Although mindfulness is not a magic solution, its health and cognitive benefits are supported by science. Studies have shown that children who engage in regular mindfulness activities may experience lower levels of anxiety and stress. They might also show improved sleep quality and fewer behavioral issues — all of which contribute to better focus during the school day.
Notably, mindfulness in classrooms can also reduce disciplinary incidents. When students are taught to observe their emotions rather than react impulsively, they tend to make more thoughtful choices. This can create a more peaceful classroom environment for both peers and educators.
Practical Considerations for Implementing These Techniques
Before introducing any mindfulness exercises, it’s essential to consider the classroom culture and the diverse needs of students. Not every child may be comfortable with quiet stillness at first. Therefore, start with short, simple exercises and gradually increase the duration or frequency based on student openness.
Teachers don’t need to be certified mindfulness instructors to implement these practices. However, participating alongside students can help model calm, attentive behavior. There are also many reputable resources and organizations that offer free, school-appropriate guides and audio tracks to support instruction.
Possible Challenges and Tips for Overcoming Them
As with any new routine, mindfulness takes time to become effective. Students may resist or find it awkward in the beginning. Consistency and encouragement are key. Remind students that being mindful doesn’t mean emptying the mind or being “perfectly calm.” Instead, it’s about gently returning their focus when it drifts — a helpful lesson in attention that extends far beyond the classroom.
Another common challenge is time constraints. However, most mindfulness activities can be done in just 1 to 5 minutes, making them easy to fit between lessons or during transitions.
Encouraging a Lifelong Skill with Lasting Academic Value
Beyond improved cognitive focus, mindfulness equips students with tools they can use throughout life. As they grow, they begin to handle academic pressures, peer interactions, and emotional ups and downs with more clarity and control. Unlike many techniques focused solely on academic outcomes, mindfulness addresses the whole child — blending mental health, emotional balance, and learning readiness.
For classrooms already dealing with high stress or behavioral disruptions, starting small with breathing or stillness can set the stage for lasting change. Over time, students often begin requesting these moments themselves, showing that mindfulness, when introduced thoughtfully, resonates deeply with young minds.
Final Thoughts on Bringing Mindfulness into the Classroom
Classroom Mindfulness Techniques for Improved Cognitive Focus provide a realistic, evidence-informed way to boost attention and reduce stress within academic settings. By creating time for stillness during the school day, teachers can foster environments that support healthier, more engaged learners.
As with any classroom tool, the success of mindfulness depends on consistency, empathy, and ongoing adaptation. Start slow, support students with patient guidance, and watch as they gradually develop greater focus, resilience, and emotional awareness — skills that benefit both their education and overall health.