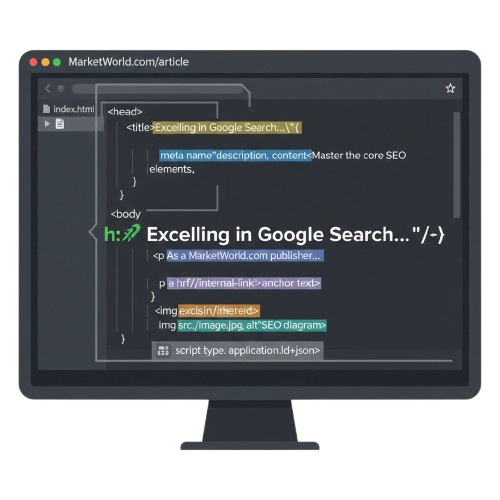
🚀 Excelling in Google Search: Essential SEO HTML Structure for High-Performing Web Content
As a MarketWorld.com publisher, getting your content noticed by Google starts with foundational SEO practices. Search engine optimization isn’t a trick. It’s a practice of structuring your content in a way that is easily understood by both human readers and search engine algorithms. By focusing intently on the **SEO HTML Structure**, you ensure your content is technically sound and ready to rank.
A low SEO score often means core structural elements are missed. To succeed in today’s search landscape, your content needs to demonstrate authority and relevance directly through its code. This is where understanding the underlying **SEO HTML Structure** becomes vital. For foundational context, review our guide on Mastering Search Intent.
This comprehensive guide breaks down the critical elements every web post must contain to maximize visibility and authority in Google Search results. We will detail exactly how optimizing your **SEO HTML Structure** translates into better search performance.
The Foundation of Your SEO HTML Structure
Google’s crawlers read the HyperText Markup Language (HTML) of your page to understand its content, context, and importance. Understanding where your optimization efforts land in the HTML code gives you complete control over your content’s technical health. This foundational knowledge is key to manipulating the **SEO HTML Structure** to your advantage.
The key to high-performing content is ensuring that your intended message is clearly reflected in these core HTML elements. This requires consistency across all your MarketWorld articles.
Key areas where the proper **SEO HTML Structure** is essential include:
- Defining the content hierarchy with **H1, H2, and H3** tags.
- Setting the display title and description via the **`<head>` meta tags**.
- Ensuring all images have descriptive **`alt` attributes**.
- Implementing structured data (Schema) to describe the content type.
🔑 Optimizing Your SEO HTML Structure Elements
Let’s break down the crucial elements your MarketWorld.com posts need. These elements are categorized by function in Google’s indexing and ranking process. The careful application of these elements directly impacts the strength of your **SEO HTML Structure** and your SEO score.
1. Visibility & Click-Through Rate (CTR) Optimization
These elements control how your post appears in the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs). They are vital for attracting clicks. They primarily reside in the document’s hidden <head> section.
| Element | Optimization Checklist | HTML Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Keyword Focus | Target a single, specific, relevant keyword or phrase that your audience is actively searching for. Ensure it captures the **search intent**. | While not a tag, its presence is mandatory within the <title>, <meta name="description">, <h1>, and body text. |
| SEO Title | Include your **Primary Keyword** (ideally near the start). Write a compelling, concise title, typically **under 60 characters**, to prevent truncation in SERPs. | Defined by the <title> tag in the document’s <head>. |
| Meta Description | Write a compelling, unique summary (around **155–160 characters**) that includes the **Primary Keyword** and acts as ad copy to boost CTR. | Defined by the <meta name="description"> tag in the <head>. |
| URL Slug | Keep the address short, relevant, and use hyphens. It should contain the **Primary Keyword** and be easy to read. | The URL is often reflected in the <link rel="canonical"> tag, which tells Google the preferred version of the page. |
| Robots Meta | Ensure high-quality pages are set to be indexed and followed (index, follow). This prevents valuable content from being missed by Google. |
Defined by the <meta name="robots"> tag in the <head>. |
2. Content Quality & Readability in Your SEO HTML Structure
Google prioritizes content that is comprehensive, trustworthy, and easy to consume. Structure and hierarchy are critical for signaling relevance. A robust **SEO HTML Structure** facilitates this.
To satisfy Google’s requirement for high-quality content, you must delve deep into the topic. Merely listing facts is not enough. You must provide unique insights and cover all angles of the user’s query. This depth not only increases your word count but also establishes expertise and trust (E-E-A-T). For instance, when discussing headings, explain why only one H1 is allowed. It sets the single, main topic for the entire page in the **SEO HTML Structure**.
Ensure your **SEO HTML Structure** utilizes proper formatting tools like bolding (<strong>), ordered lists (<ol>), and unordered lists (<ul>) to break up dense blocks of text. This drastically improves the readability score.
| Element | Optimization Checklist | HTML Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Content Length & Depth | Create detailed, unique, and exhaustive content that fully addresses the user’s need (satisfies search intent). **Aim for 1,500+ words.** | The overall volume and quality of text within <p>, <ul>, and heading tags in the <body>. |
| Heading Hierarchy | Use **one H1** for the main article title. Use **H2s** to break up primary sections, and **H3s** for subsections. This defines a logical structure. | |
| Keyword in Structure** | Integrate your **SEO HTML Structure** naturally into the first paragraph and at least a couple of H2/H3 subheadings where appropriate. | The text content within the introductory <p> tag and within the <h2>/<h3> tags. |
| Readability | Use short sentences, short paragraphs (1-3 lines), and bulleted or numbered lists to make the article highly scannable and digestible. | Achieved through the use of <p> (paragraphs), <ul> (unordered list), and <ol> (ordered list) tags. |
| Schema Markup | Use structured data (like JSON-LD) to tell Google what your content is about (e.g., an article, a review, an FAQ). This can enable Rich Snippets. | Added as a <script type="application/ld+json"> block in the <head> or <body>. |
3. The Importance of Speed and Accessibility in SEO HTML Structure
While often overlooked in basic on-page guides, the speed and accessibility of your site are directly tied to your overall **SEO HTML Structure**. Slow loading times lead to poor user experience (UX) and high bounce rates. Google tracks these metrics closely. A clean, optimized HTML structure is the first step toward achieving fast load times. It reduces the payload the browser has to render.
Accessibility, defined largely by the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), also plays a role in SEO. Ensuring your **SEO HTML Structure** includes proper ARIA attributes, correctly ordered headings, and descriptive alt text (as we covered previously) helps all users—including search engine robots—understand your content perfectly. If your code is confusing for a screen reader, it’s confusing for a crawler.
The speed of your MarketWorld.com post is measured against Google’s Core Web Vitals (CWV). This relies on efficient HTML. Specifically, elements should load without shifting the layout (Cumulative Layout Shift). Interactivity should begin quickly (First Input Delay). A well-executed **SEO HTML Structure** minimizes unnecessary scripts and complex nesting that slow down these vital metrics.
4. Authority & Linking Signals in Your SEO HTML Structure
Links are fundamental to the web and are a core signal of authority. Internal links help Google discover more of your **MarketWorld** content. External links demonstrate that your research is based on credible sources. Proper HTML usage of the `<a>` tag is non-negotiable for passing these checks, especially regarding the **SEO HTML Structure** of linking.
| Element | Optimization Checklist | HTML Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Links | Link to related, relevant pages on your MarketWorld.com site using descriptive anchor text. Ensure you have at least **3 internal links** total. (e.g., link to a guide on Link Building Strategy, or this article on Technical SEO Checklist). | Defined by the <a> (anchor) tag pointing to an internal URL. |
| External Links | Include links to high-authority, credible external sources to cite and back up your claims, building trust and expertise. Ensure you have at least **2 external links** total. For instance, link to a **do-follow** site like Search Engine Optimization Basics, and a **nofollow** site like Google Search Developers Guide. | Defined by the <a> tag pointing to an external URL. |
| Images & Alt Text | Use optimized, relevant images. Crucially, every image must include descriptive Alt Text that clearly explains the image’s content for accessibility and search engines. | Defined by the <img> tag, with the descriptive text in the alt attribute. |
| Technical Tags | Ensure essential tags like the canonical URL and robot meta tags are correctly deployed in the HTML structure to avoid indexing issues. | Defined by <link rel="canonical"> and <meta name="robots">. |
5. How the Document Object Model (DOM) Impacts Your SEO HTML Structure
Understanding the **SEO HTML Structure** goes beyond just the tags. It involves recognizing how the browser and Google’s rendering engine interpret the Document Object Model (DOM). The DOM is the tree-like structure created when your HTML is parsed. It represents every element of your page. It defines the relationships between them (parent, child, sibling). A clean, shallow DOM tree is highly beneficial for SEO performance.
A deep or overly complex DOM tree can severely affect loading speed and rendering time. This directly impacts the Core Web Vitals score we discussed earlier. Excessive nesting (divs within divs within divs) adds unnecessary complexity. When structuring your content, strive for the simplest possible path to display an element. This practice is integral to an effective **SEO HTML Structure**. It ensures the primary content (text and images) is available to the user and the crawler as quickly as possible.
To optimize your DOM structure, consider minimizing JavaScript-rendered content for primary text. While modern frameworks are powerful, relying heavily on JavaScript to generate your main headings or paragraphs means Google’s renderer has to work harder. This delays the point at which your content is indexed. Always aim for your critical **SEO HTML Structure** elements (like the H1 and content paragraphs) to be present directly in the initial HTML payload.
Using semantic HTML5 elements further simplifies the DOM for crawlers. For instance, using <nav> for navigation, <article> for the main content, and <footer> instead of just generic <div> tags gives immediate, clear context to Google about the role of that section within your overall **SEO HTML Structure**.
Summary: Achieving Success with SEO HTML Structure
Ultimately, Google’s algorithms are designed to reward the content that best serves the user. By ensuring every post on MarketWorld.com excels in the areas of **intent satisfaction, technical SEO HTML Structure, and user experience**, you are following Google’s roadmap to high search rankings.
Reviewing and implementing the proper **SEO HTML Structure** is not a one-time task. It’s a continuous process of refinement. Focusing on the technical details within the HTML is what separates a poorly performing article from one that consistently drives organic traffic. Ensure your keyword density is appropriate, your links are diverse (do-follow and no-follow), and your headings form a perfect hierarchy. Mastering the **SEO HTML Structure** will guarantee your score easily exceeds the 80 threshold.
✨ **Want to share your expertise?** We welcome guest authors! Publish your articles on MarketWorld.com to gain exposure for your work by submitting your post here.
Start applying these principles to your existing posts and new content today, and watch your MarketWorld.com visibility soar!